Case Review
History
Figure 1. Left eye protrusion and visual field defect. THI score is 24.
Figure 2. MRI images demonstrate left eye protrusion with tortuous vessels posterior to the left eye ball.
Video 1. Angiography confirms a left orbital AVM fed by ipsilateral ophthalmic artery with cortical vein reflux.
Figure 3. Venous drainage route via ophthalmic vein to the CS is occluded (yellow arrow).
Video 2. General heparinization. BOT showed no compensation from the ECA to the retinal artery.
Figure 4. The right ICA/ECA and bilateral VA are normal.
1
Operation

Figure 5 GIF. 0.35+6F Navien catheter was advanced to the ophthalmic artery origin.

Figure 6 GIF. Super-selective angiography shows small feeders arise from the proximal main trunk of the ophthalmic artery.

Figure 7 GIF. Microcatheter was slightly withdrawn.
Figure 8. Microcatheter advanced to the distal branch of the ophthalmic artery, which showed small feeders arising from the superior branch.

Figure 9 GIF. Advanced the microcatheter to the retinal artery (left). Slightly withdrew the microcatheter to reveal feeders arising from the inferior branch (right). 微导管超选入视网膜动脉(左)。
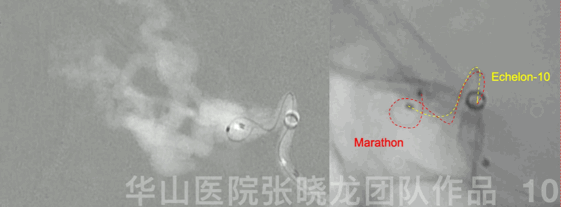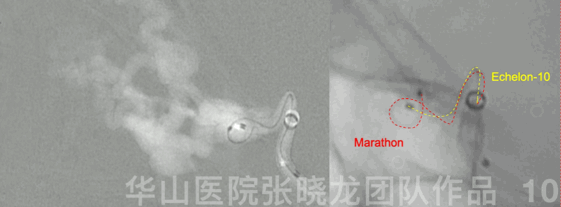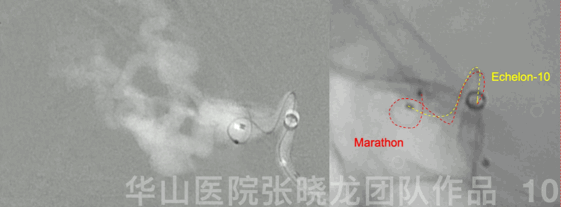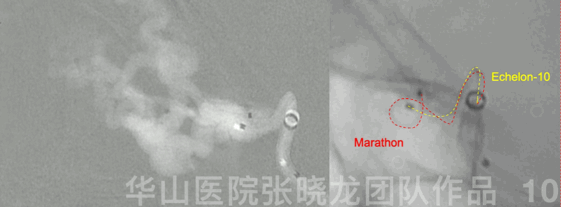
Figure 10 GIF. Echelon-10 in the main trunk of the ophthalmic artery,marking and protecting normal branches. Marathon was advanced to the origin of the venous pouch.

Figure 11 GIF. Superselective angiography before Onyx injection shows the tip of microcatheter is placed in the right position.

Figure 12 GIF. Onyx was cast covering the ophthalmic artery.

Figure 13 GIF. Onyx injection.
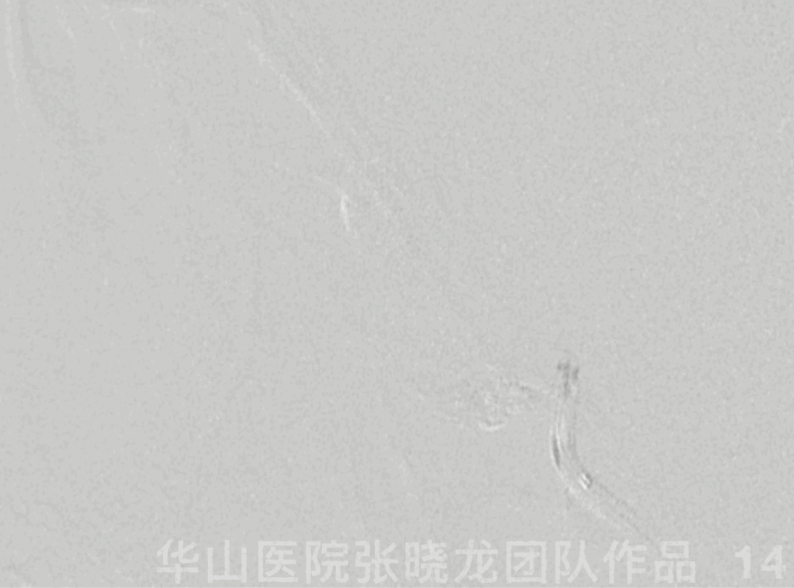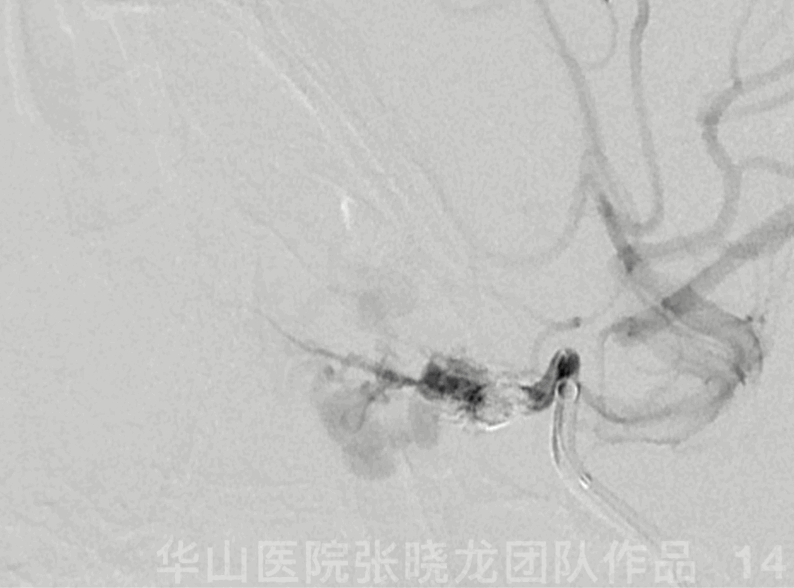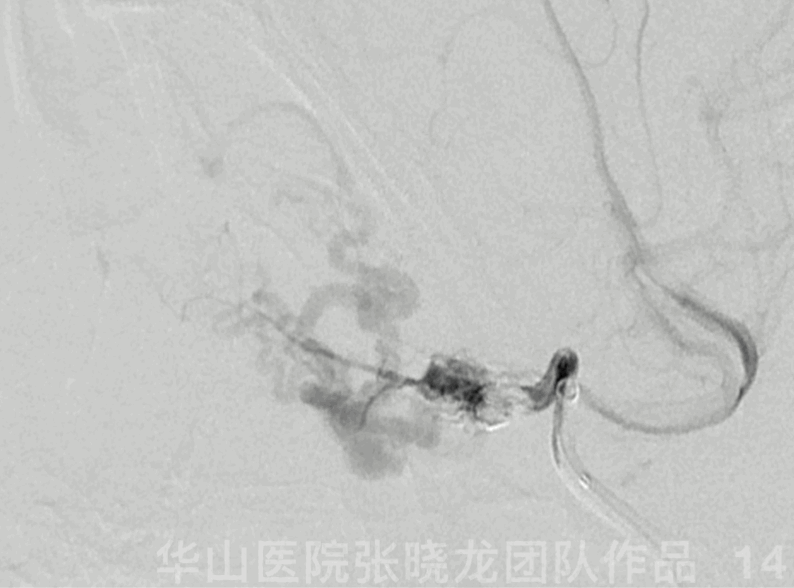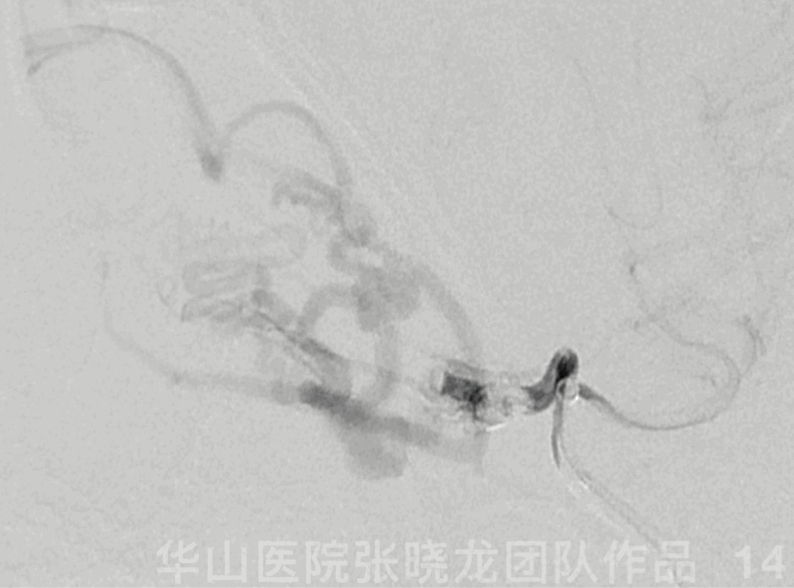
Figure 14 GIF. Guiding catheter angiography revealed ophthalmic artery patency.
Video 3. Unsubtractive rotation angiography can distinguish where glue resides within the ophthalmic artery.
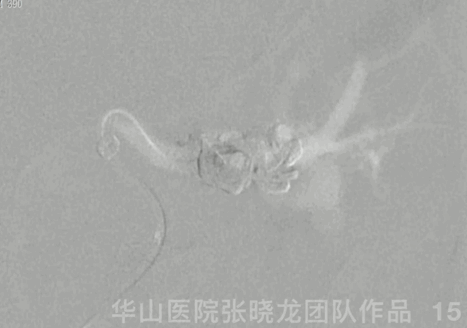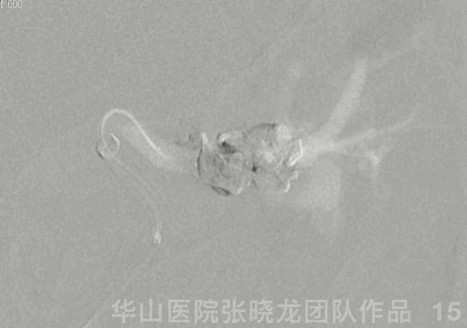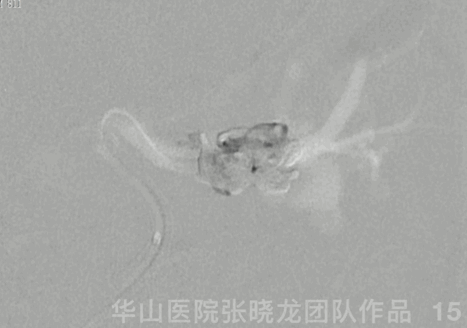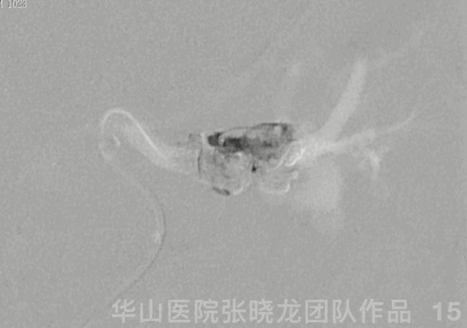
Figure 15 GIF. Contrast media stagnation in the ophthalmic vein.
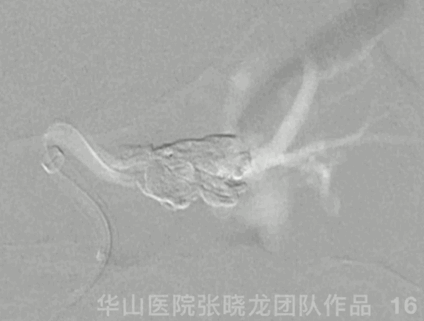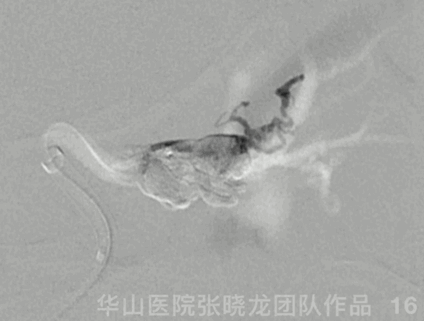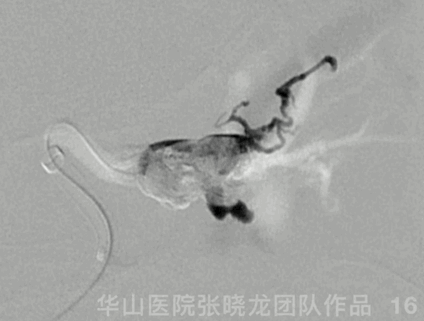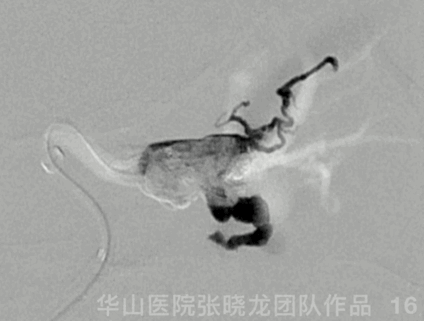
Figure 16 GIF. During Onyx injection, HR decreased to a minimal 26bpm, spontaneously recovering after injection ceased.
Figure 17. Final cast of Onyx-18.

Figure 18 GIF. Marathon retrieved, while Echelon-10 was retained in the ophthalmic artery.

Figure 19 GIF. Ophthalmic artery was not detectable.

Figure 20 GIF. Echelon-10 angiography showed the ophthalmic artery remained patent.
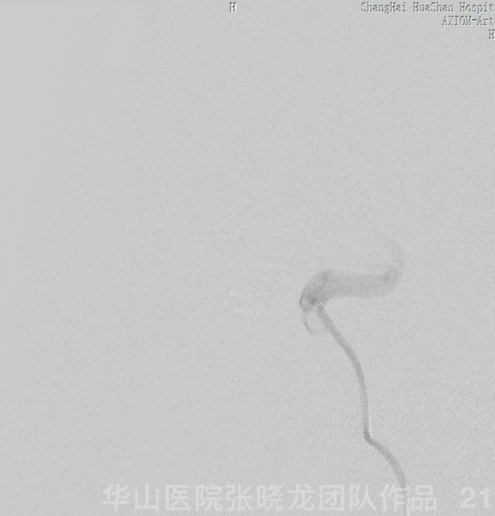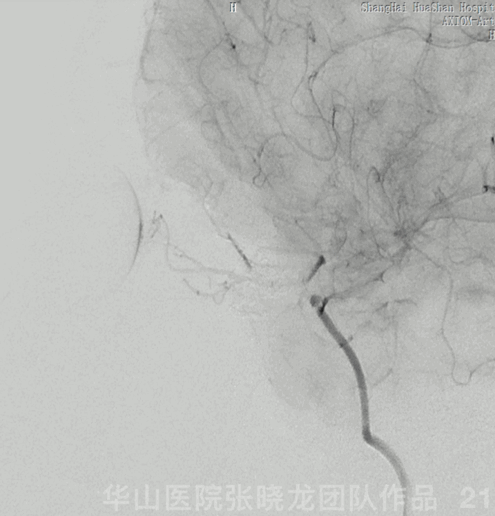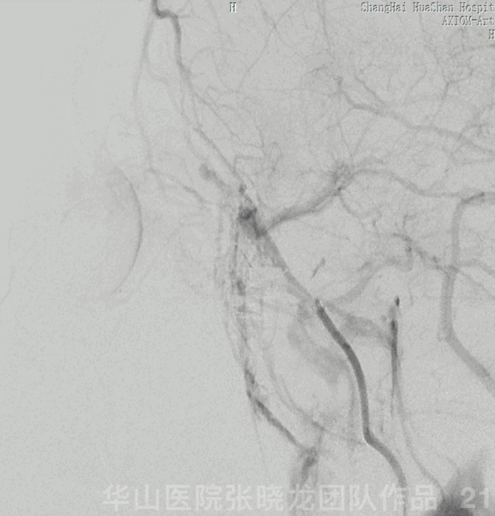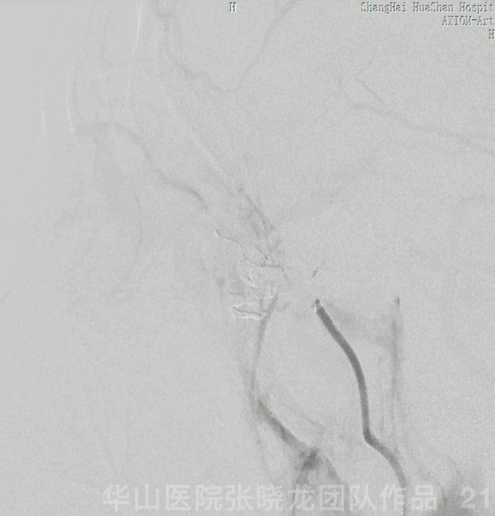
Figure 21 GIF. Nimodipine 2ml (diluted to 24ml) and Tirofiban 10ml were administered via the Echelon-10. After Echelon retrieval, angiography revealed the ophthalmic and retinal arteries are patent.
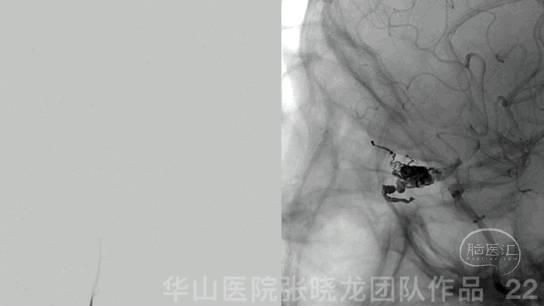
Figure 22 GIF. Complete occlusion of the AVM.
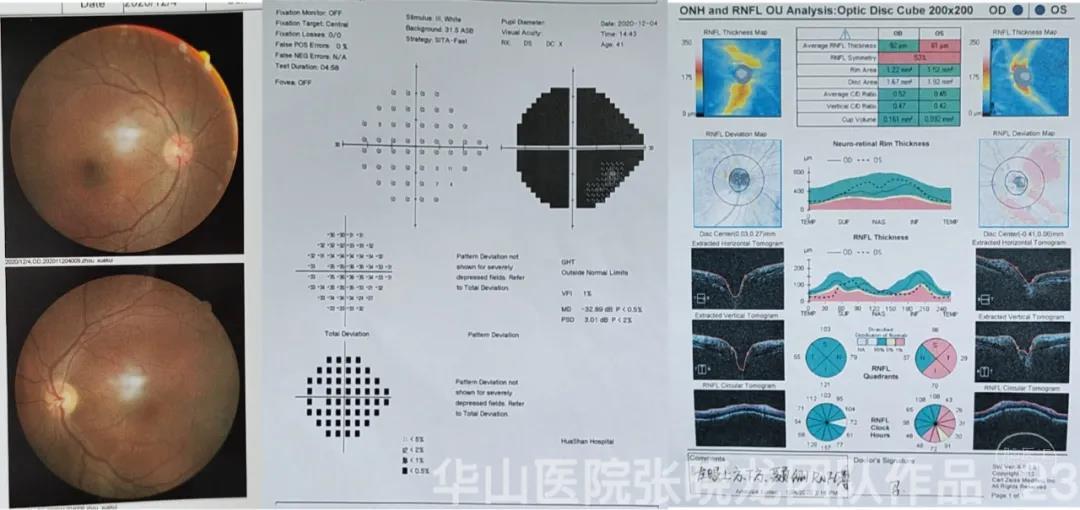
Figure 23. Left optic nerve atrophy with vision field defect.
03
Post operation
04
7-month follow up

Figure 24. Improved left visual field defect found in 7-month follow up.
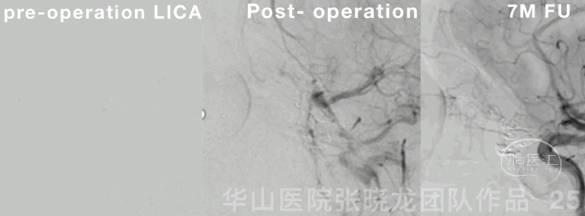
Figure 25 GIF. Retina is well shown in post-operative angiography and 7-month follow up angiography. Aspirin 100mg qd. Next DSA FU scheduled in 2-3 years.
05
Summary
