Published in November 9, 2023
ACA A2-A3 dissecting AN Two stage embolization
• CC: The patient suffered a headache, and CT scan showed subarachnoid hemorrhage in June 2017. • PE: The clumsy right limb and left limb hypoesthesia.• Past medical history: smoking 10+ years, half pack per day, quitting about 2 years. • NE: Left limb hypoesthesia; Babinski (-).
Figure 1 GIF. Callosum and intraventricular hemorrhage. 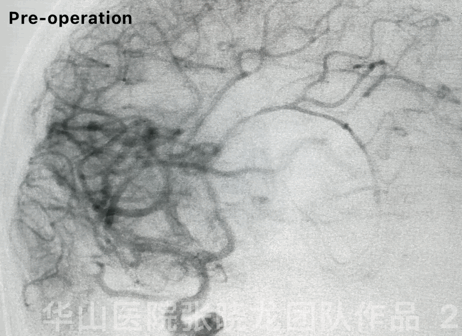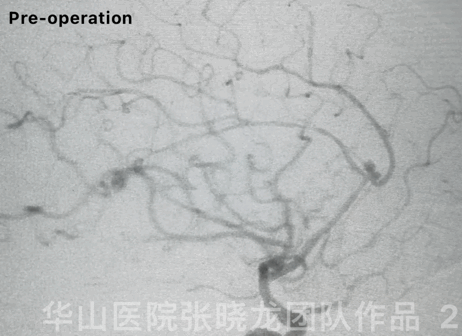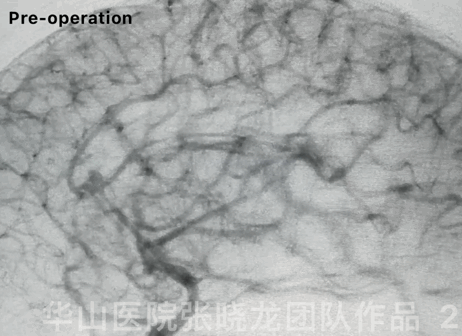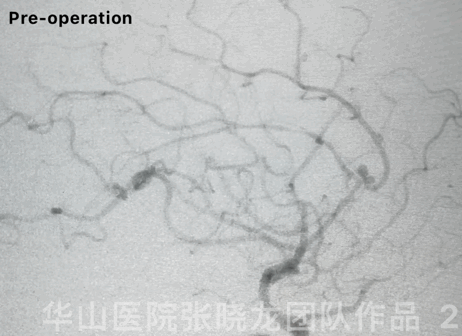
Figure 2 GIF. Rotational DSA confirms a ruptured pericallosal aneurysm with irregular shape and daughter sacs.• Ruptured pericallosal aneurysm with irregular shape and daughter sacs indicated high re-rupture risk, which should be treated as soon as possible.
• To avoid perioperative bleeding and antiplatelet drugs, simple coiling was adopted in the acute phase of aneurysmal hemorrhage. If the aneurysm recurred, stent-assisted coiling was used in the second stage. • Both sacs of the aneurysm need to be packed densely with dual microcatheters.
Video 1. The aneurysm with two daughter sacs was densely packed by the dual microcatheter technique.
Video 2. Post-operative angiography shows the aneurysm neck is overpacked with the slow flow in the front branch of ACA
Video 3. Six-month follow-up angiography shows mild relapse at the aneurysmal neck.
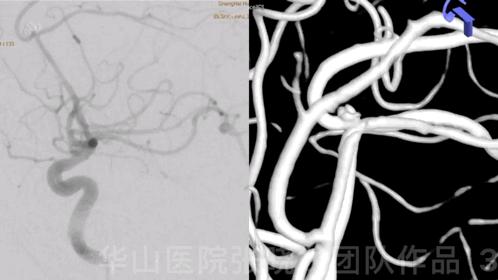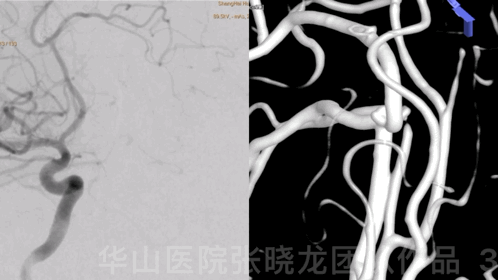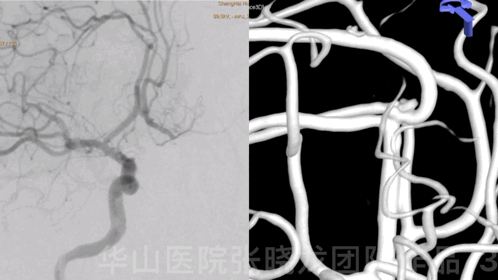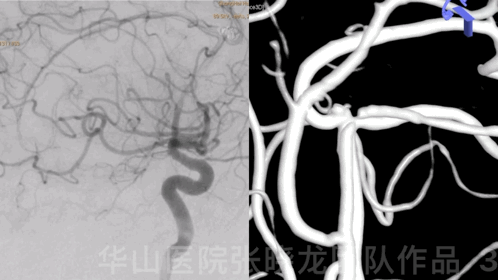
Figure 3 GIF. 18-month follow-up angiography demonstrates enlarged aneurysmal neck relapse.
Second stage treatment strategy
• Though the aneurysm was densely packed, the aneurysm neck relapsed and enlarged on 6-month and 18-month follow-up respectively, which indicated the neck was unstable. Therefore the relapsed aneurysm should be treated.
• Direct blood flow impingement may lead to recurrence. Therefore, a stent-assisted coiling technique was adopted in the second stage to straighten the parent artery and remodel the hemodynamics to decrease recurrence risk.
Figure 4 GIF. Measurements. Residual sac: 2.08*1.44mm; parent arteries: 1.40-1.54mm.
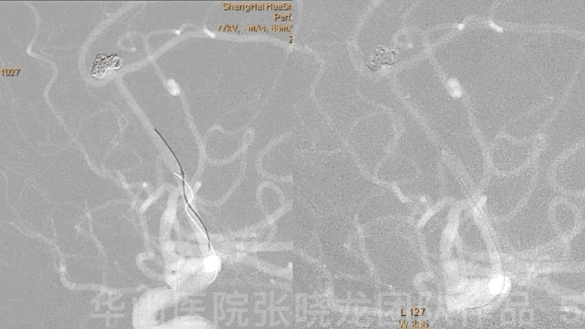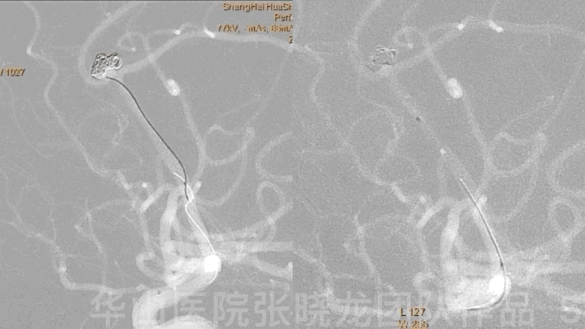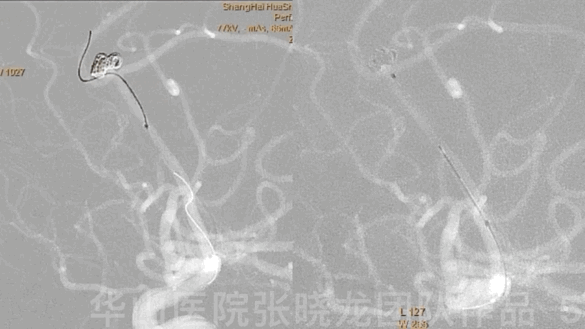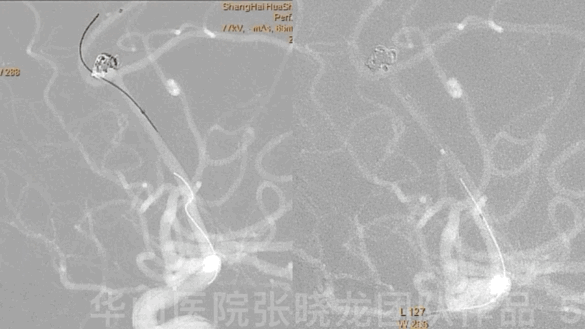
Figure 5 GIF. A headway-21 microcatheter with a preshaped tip was navigated to the right callosomarginal artery. An Echelon-10 microcatheter with a straight tip was sent to the residual aneurysmal sac.
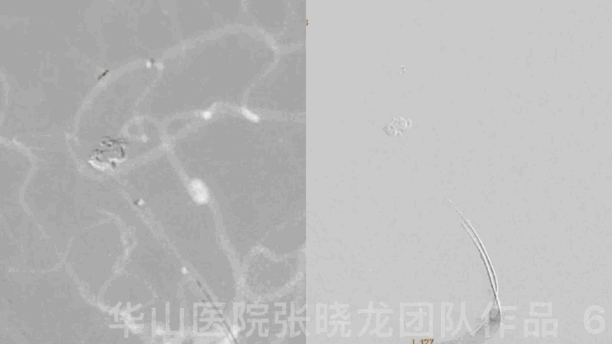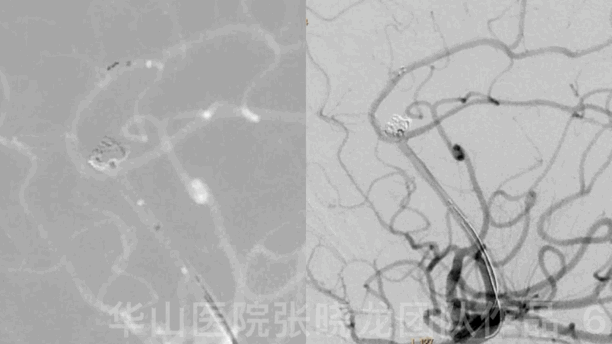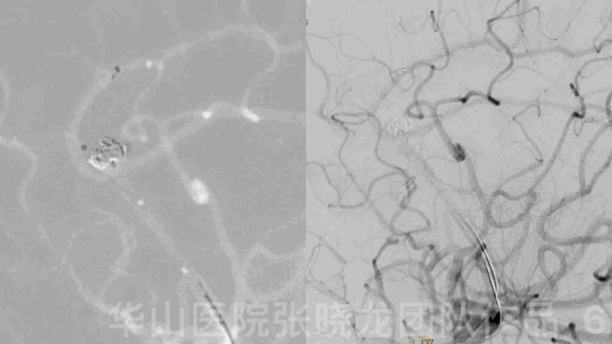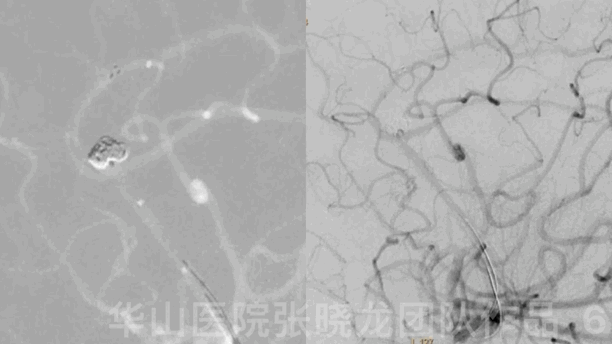
Figure 6 GIF. A Solitaire 4mm*20mm stent was deployed via the Headway-21 microcatheter.

Figure 7 GIF. A Hypesoft 2mm*3cm coil could not form a satisfied basket and protrude into the parent artery. It was retrieved.

Figure 8 GIF. A Hypersoft 2mm*6cm coil was inserted into and densely packed the residual sac.

Figure 9 GIF. The aneurysm was densely packed with parent artery patent. Intact intracranial vessels are noted. Tirofiban 15ml was administrated via the guiding catheter.
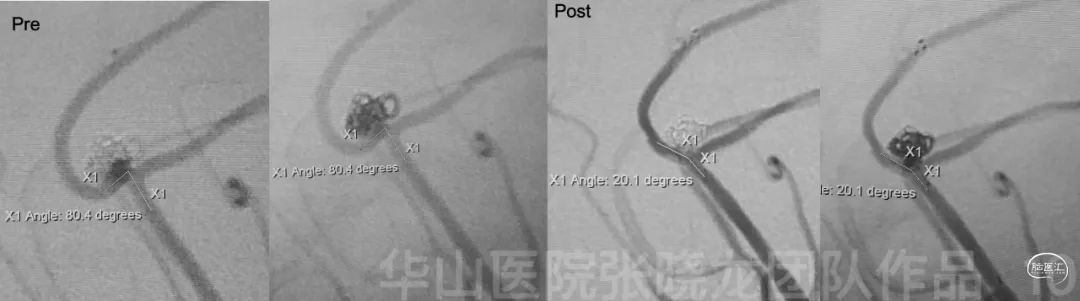
Figure 10. Straightened parent artery angle is noted compared to the parent artery angle of the relapsed aneurysm.NE: GCS 15, Left limb hypoesthesia, bilateral limb strength normal, Babinski (-).
Medication: Tirofiban 15ml/h sustained 48 hours. • Clopidogrel 75mg for 3 months and Aspirin 100mg for long-term.
• Control and monitor the blood pressure.
• Follow up was scheduled in a year.
• The patient felt left limb numbness and right limb clumsy • Medication: Clopidogrel 50 mg qd for one year
• Follow up: 3-5 year DSA

Figure 11 GIF. Eleven month after the stent assisted coiling for the residual sac at 18-month follow-up, the angiography shows no relapse and the parent artery patent.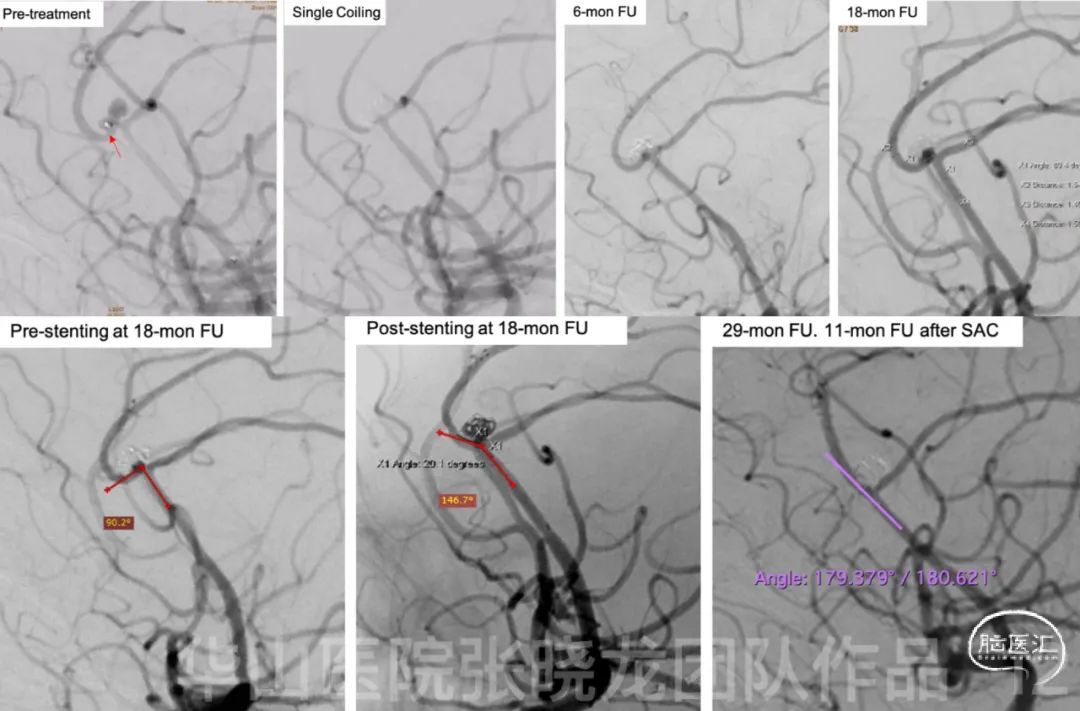
Figure 12. Review of treatment stages and follow-up. After SAC, a significantly straightened parent artery is observed at post-stenting and follow-up angiography.6• Indication: Ruptured pericallosal aneurysm with irregular shape and daughter sacs indicated high re-rupture risk, which should be treated as soon as possible.
• Treatment strategy: To avoid perioperative hemorrhage and antiplatelet drugs, simple coiling was adopted in the acute phase of aneurysmal hemorrhage. If the aneurysm is recanalized, stent assisted coiling can be used at the second stage. In this case, the unstable aneurysm neck relapsed and enlarged in follow-up, SAC was performed. • Techniques: Both sacs of the aneurysm need to be packed densely with dual microcatheters. Advantage of SAC at the second stage: • Direct blood flow impingement may lead to the recurrence. Therefore, stent assisted coiling technique was performed at the second stage for changing the hemodynamics to decrease recurrence risk.
• Stent-induced vessel straightening combined coil embolization has the best performance in hemodynamic modifications and may reduce the recurrence rate for intracranial bifurcation aneurysms1.
• Solitaire stent possessed low thrombogenicity. For intracranial bifurcation aneurysms, Solitaire stent-assisted coiling induced favorable parent artery angular remodeling and achieved a significantly low recurrence rate2.

![article]()
Comments
Log into post your comments













