Review
History
• CC: Suffered from blurred vision for a month. Local hospital MRI revealed a left ophthalmic aneurysm ( not available) .
• NE: Identify finger count from 15cm, left temporal visual field defect ( without specialized eye exams).
• Past medical history: Congenital deafness in the left ear; Cholecystectomy 7 years ago; Duodenal ulcer.
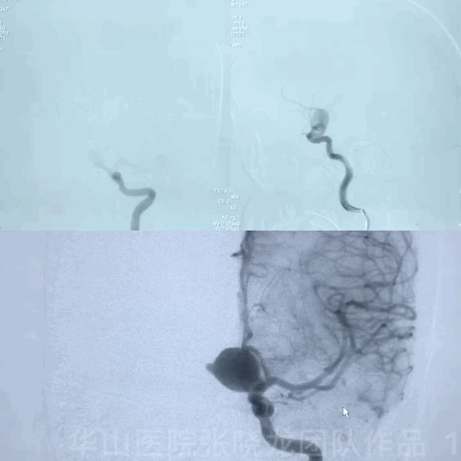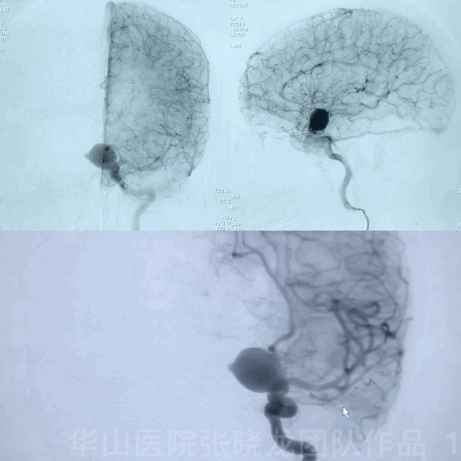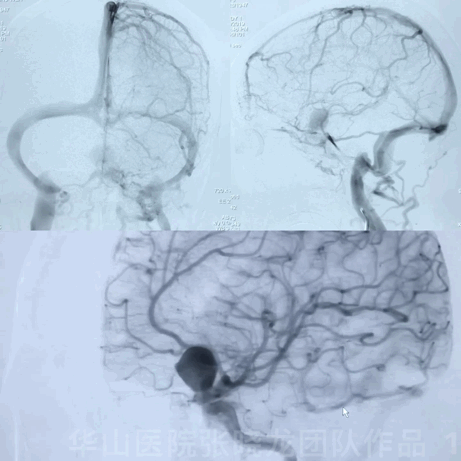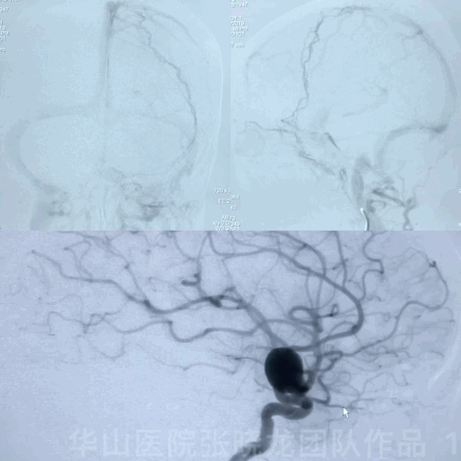
1
Treatment Strategy
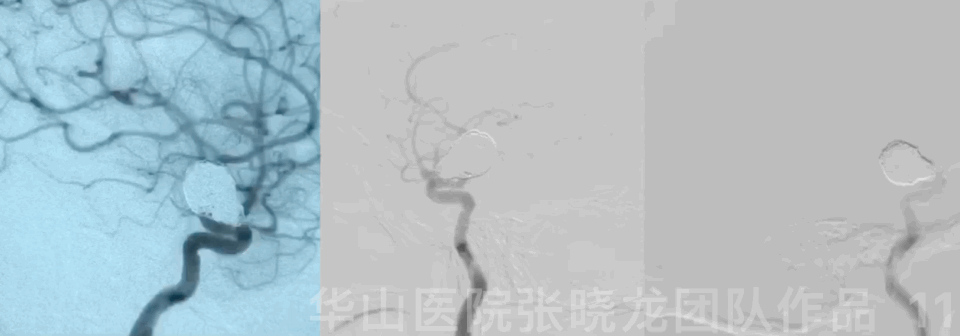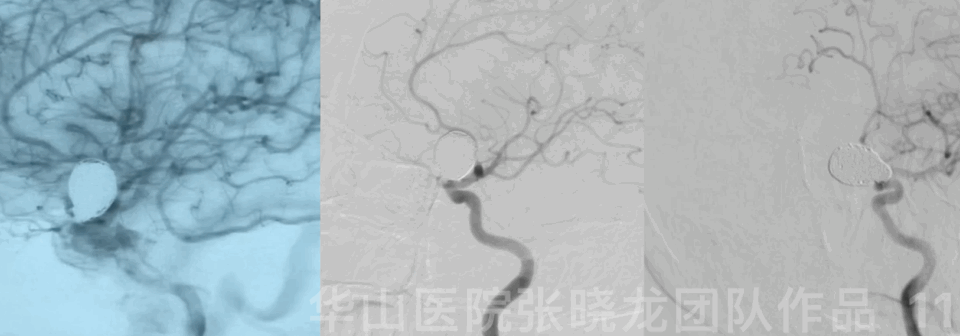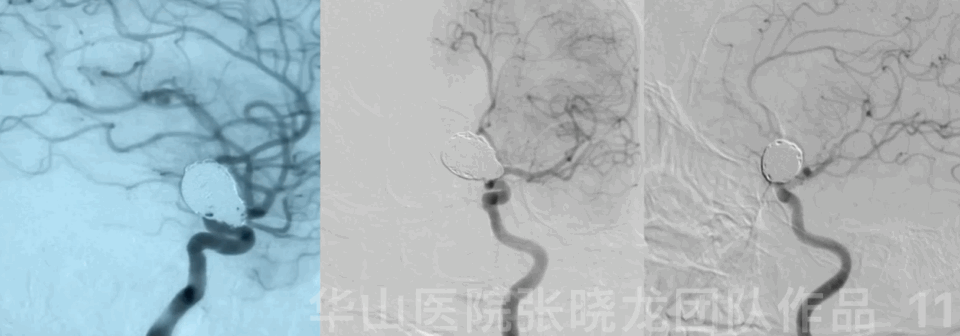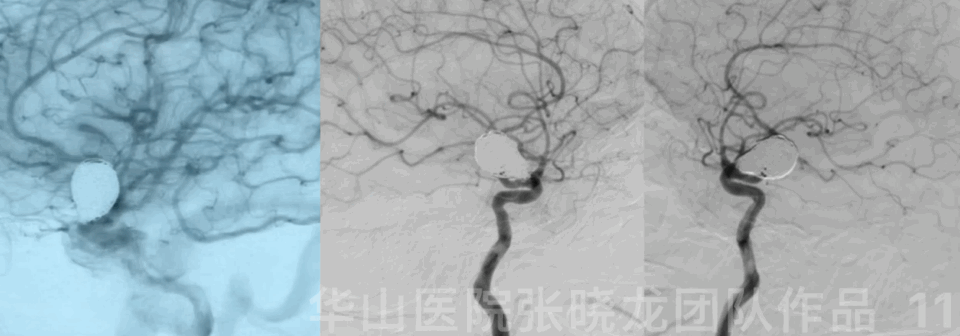
• Irregular left large upper-medial ophthalmic aneurysm with mass effect should be treated.
2
Operation

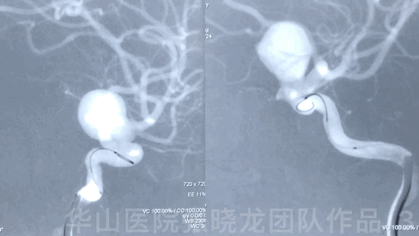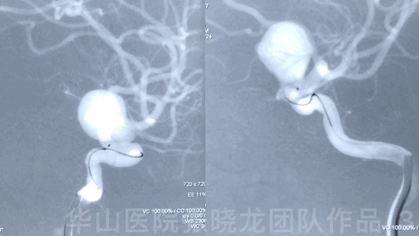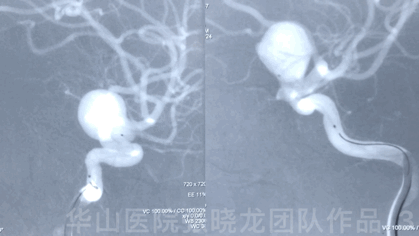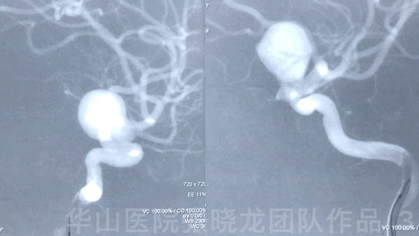
Video 1. Microplex18 Cosmos Complex 20mm*65cm was inserted into the aneurysmal sac for framing.

Video 2. Insert a Microplex18 Helical Regular 8mm*30cm coil.
视频 2. 填入1枚Microplex18 Helical Regular 8mm*30cm弹簧圈。
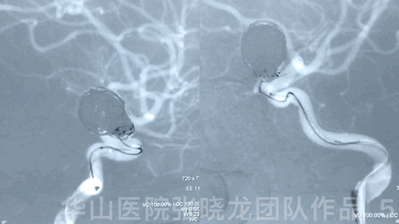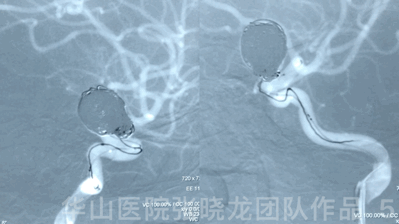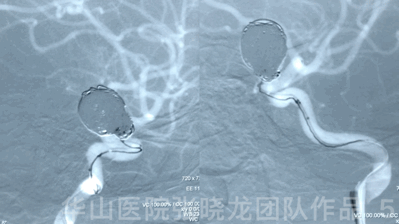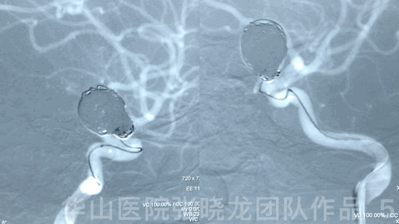
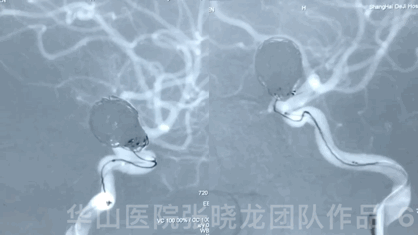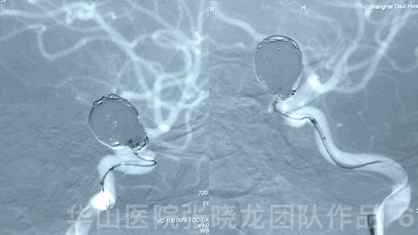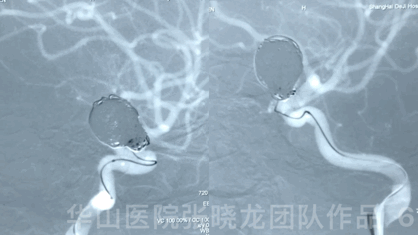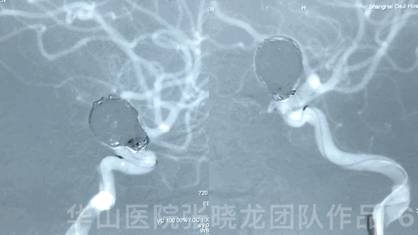

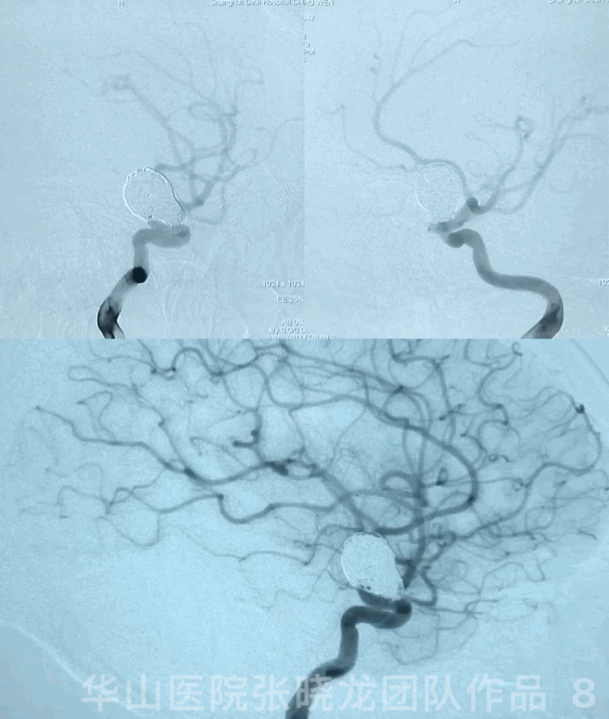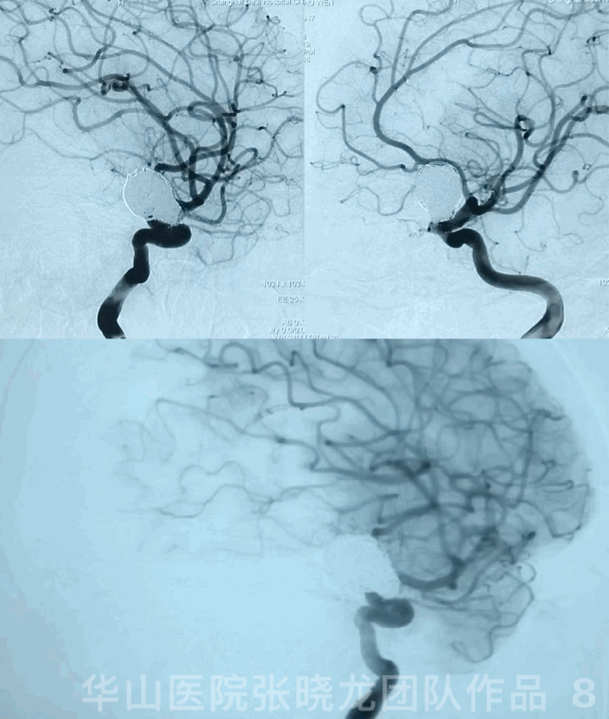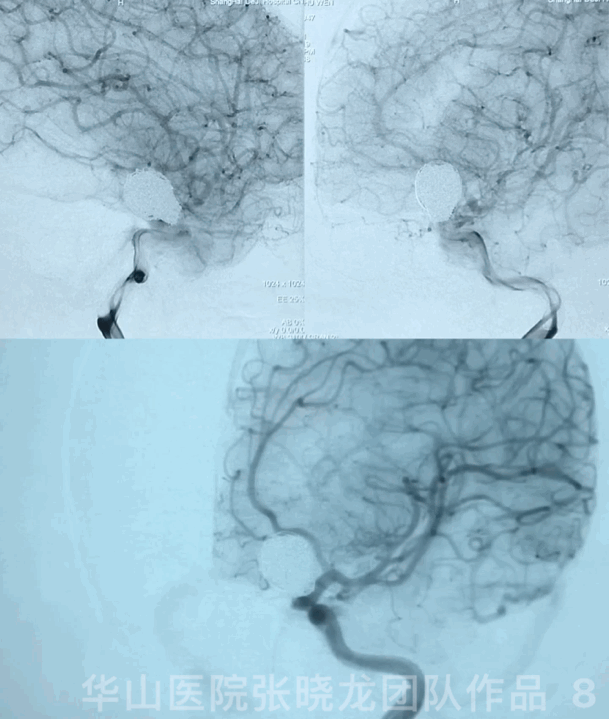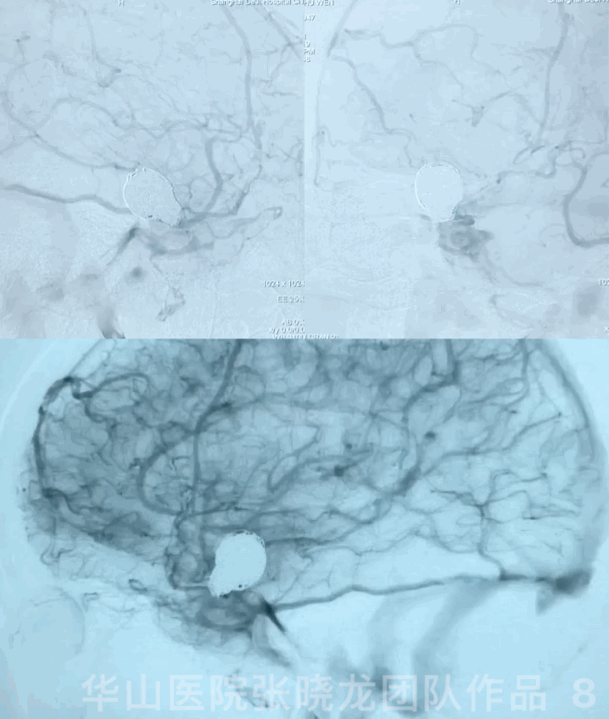
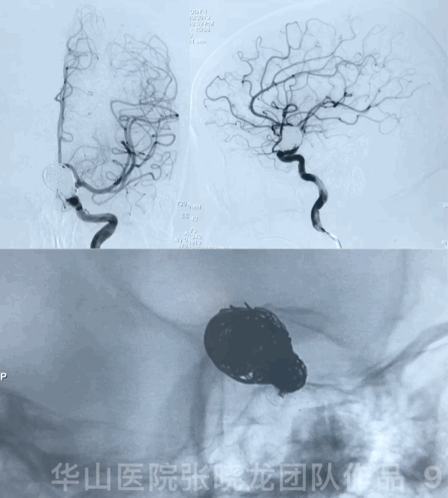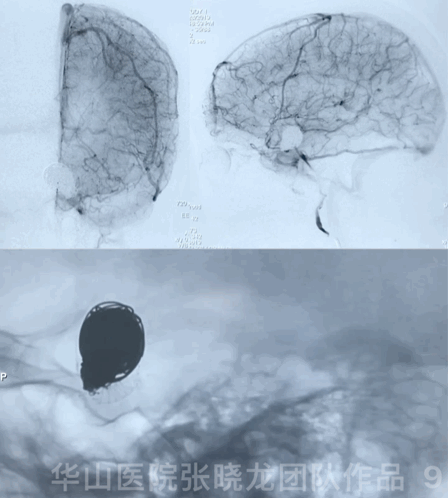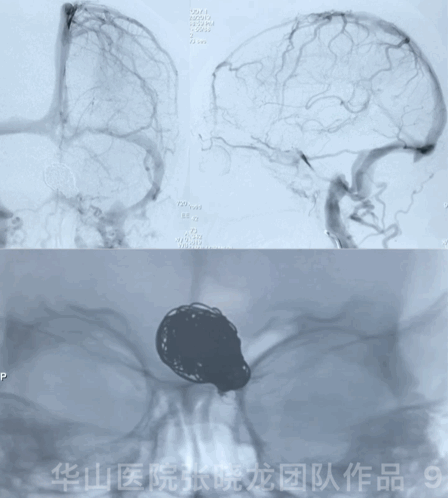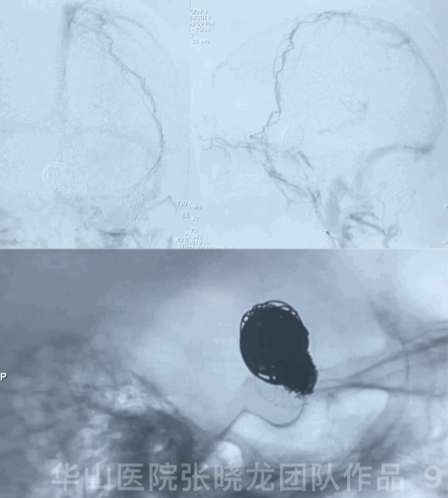
3
Post Operation
• TEG: ADP 10.7%.
• Medication: Suggest dual antiplatelets at least 3 months. However the patient stopped antiplatelets 2 months after operation.
4
Follow-up (4-month, 38-month)

• The patient still suffered from blurred vision and eye exams showed bilateral eye field defect.

6
Summary
Left large upper-medial ophthalmic aneurysm with mass effect should be treated.
This case adopted the stent-assisted large coiling technique. Block by Block embolization was performed to pack the sac with large coils and embolize the neck with small coils, which can decrease the recurrence rate while the mass effect may remain existed. Large coils for aneurysm sac provided strong support and LVIS assisted small coils for aneurysm neck embolization to decrease neck relapse. Large coiling technique could lower recurrence rate while mass effect may remain existed. A pipeline could be chosen to alleviate mass effect for this case. Coil selection is significant in this case. Though the first two coils did not provide a satisfied frame, the stable basket involving the neck was achieved by the third coil framing. The right ophthalmic aneurysm is regular and small, indicating the low risk of rupture. It coud be follow-up.
