Review
68 y/o, female.
• CC: Suffered from dizziness 12 days ago. CTA revealed a right ophthalmic aneurysm with wall calcification.
• Medical history: HTN for 20 years, controlled well; high blood sugar without medication.
• Medication: Felodipine, Candesartan.
• PE: (-)


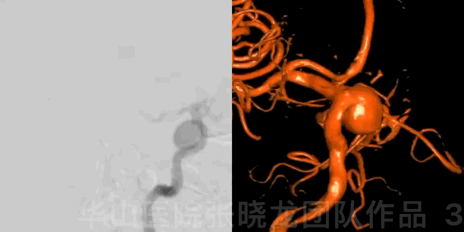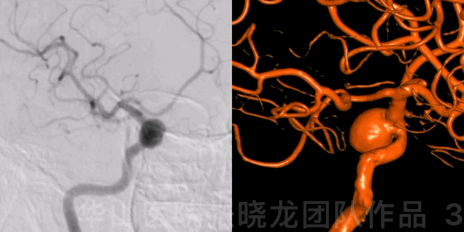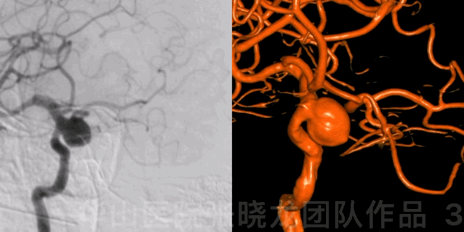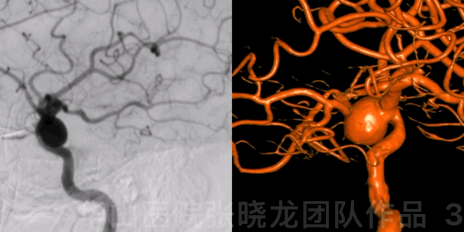
Figure 3 GIF. DSA confirmed a large right posterior-wall ophthalmic aneurysm.
1
Strategy
• Large carotid ophthalmic aneurysm should be treated to avoid rupture and further mass effect.
• Dual microcatheter technique was adopted to coil this large aneurysm.
• Large coil technique with large stiff coiling microcatheter (prowler plus) was adopted to afford strong support for stability, which could decrease the recurrence rate.
• Guiding catheter should be advanced as far as possible to supply strong support.
• Pipeline was another choice for this kind of large ophthalmic aneurysms.
2
Operation
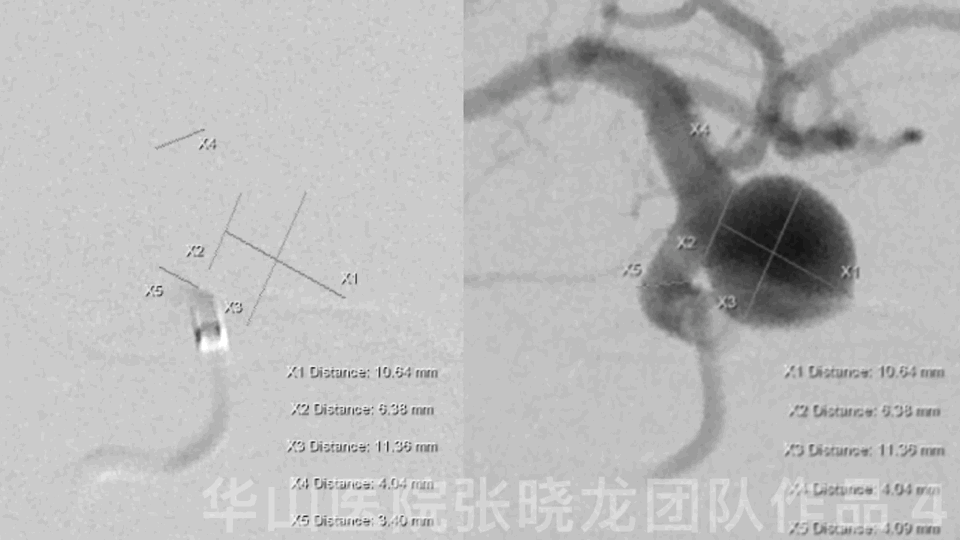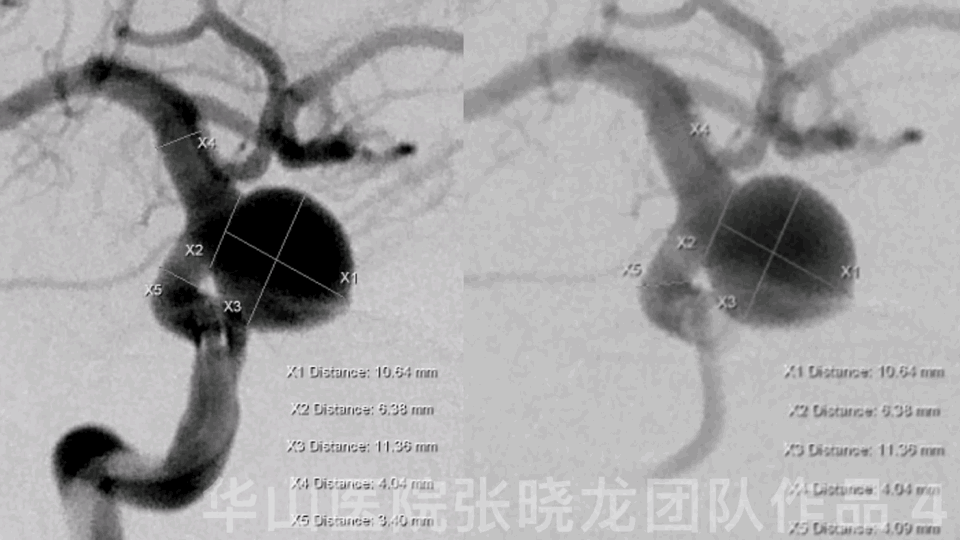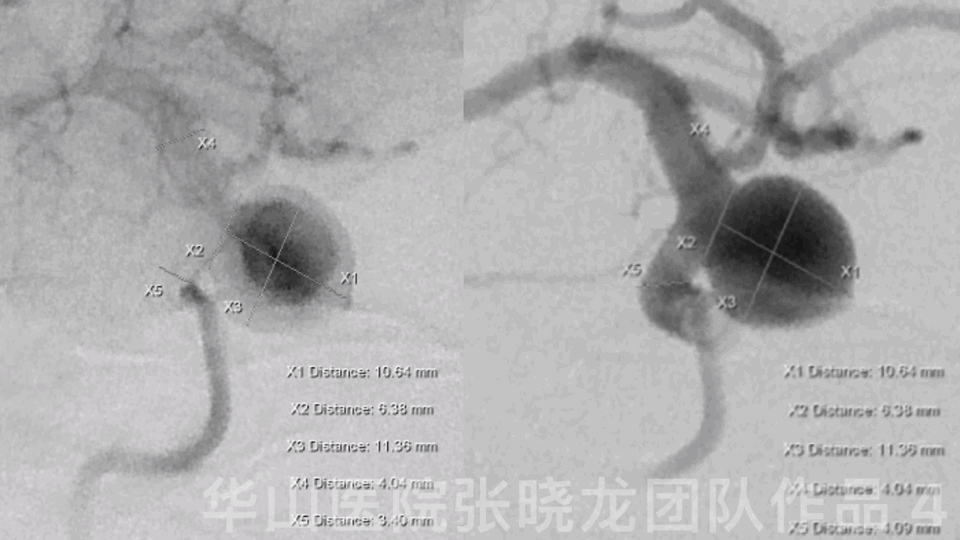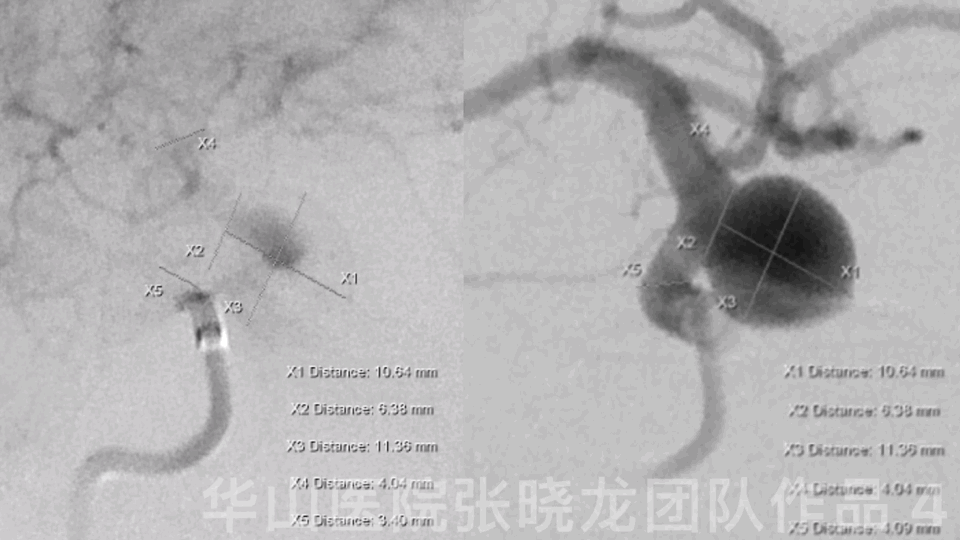
Figure 4 GIF. General heparinizations
6F Envoy DA
Measurements:
AN size: 11.13*11.29mm
AN neck: 6.14mm
Proximal parent artery:3.93mm
Distal parent artery:3.70mm
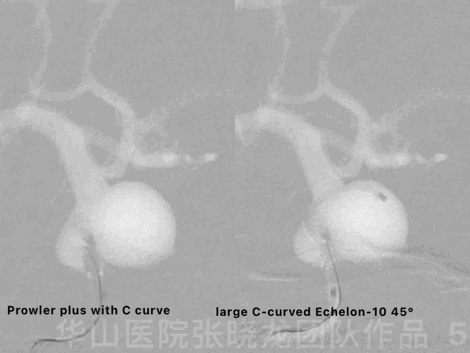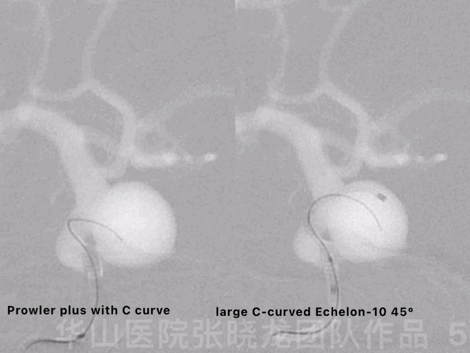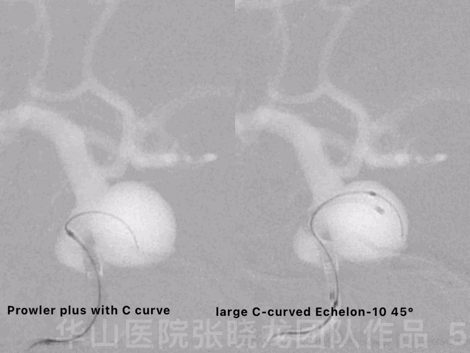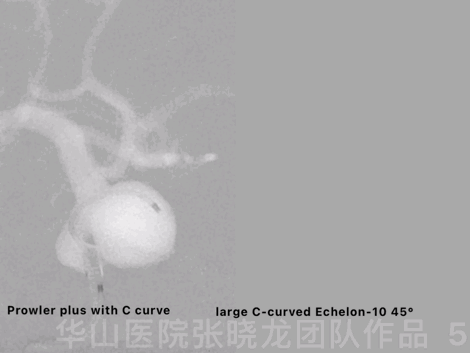
Figure 5 GIF. The aneurysm was packed by dual microcatheter technique. Prowler plus with C curve was navigated into the aneurysm sac with the guiding of a Synchro-II. A large C-curved Echelon-10 45° was advanced into the sac.
Video 1. The first coil was Perdenser 14mm*30cm and formed a satisfied basket. Insert the following coils in sequence: Three Perdenser 14mm*30cm, two Perdenser 12mm*30cm and one Perdenser 10mm*30cm.

Figure 6. Attempt to insert a Perdenser 5mm*20cm coil but failed. Retrieving prowler plus microcatheter.
Video 2. Place a XT-27 microcatheter into the right M1 segment by the support of Synchro-II. Deploy a Neuroform 4*15mm at the aneurysm neck.
Video 3. Three coils above were inserted successfully into the aneurysm through Echelon-10 45°. The aneurysm was packed densely.

Figure 7 GIF. 1ml Nimodipine and 10ml Tirofiban were administered.
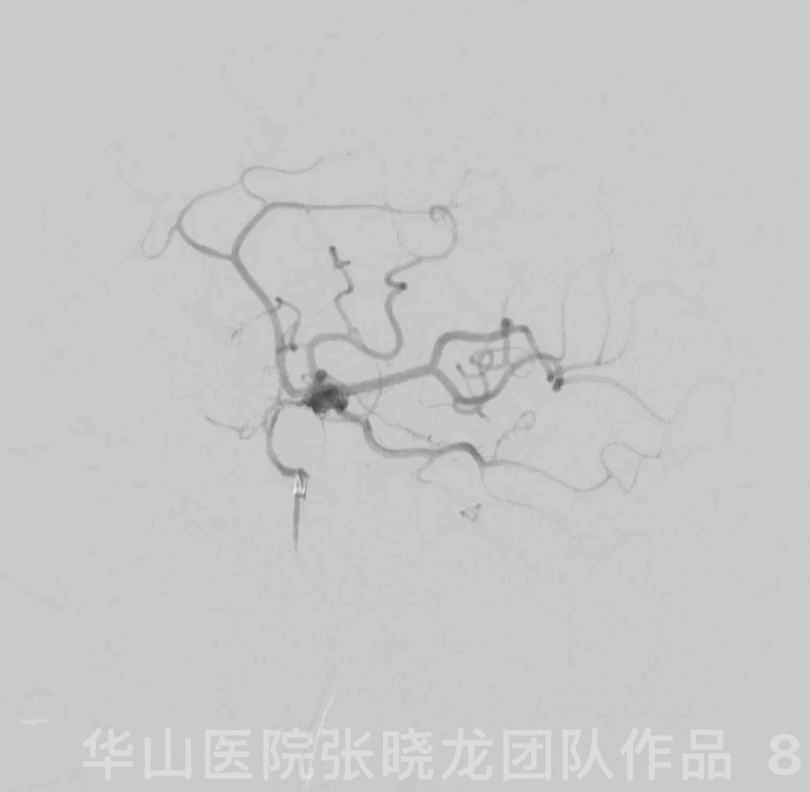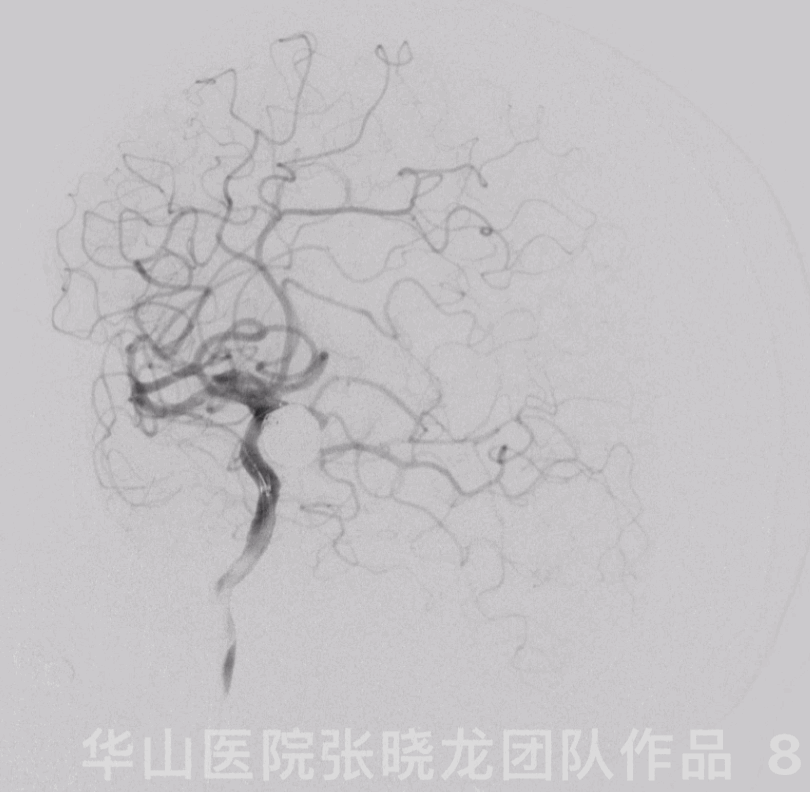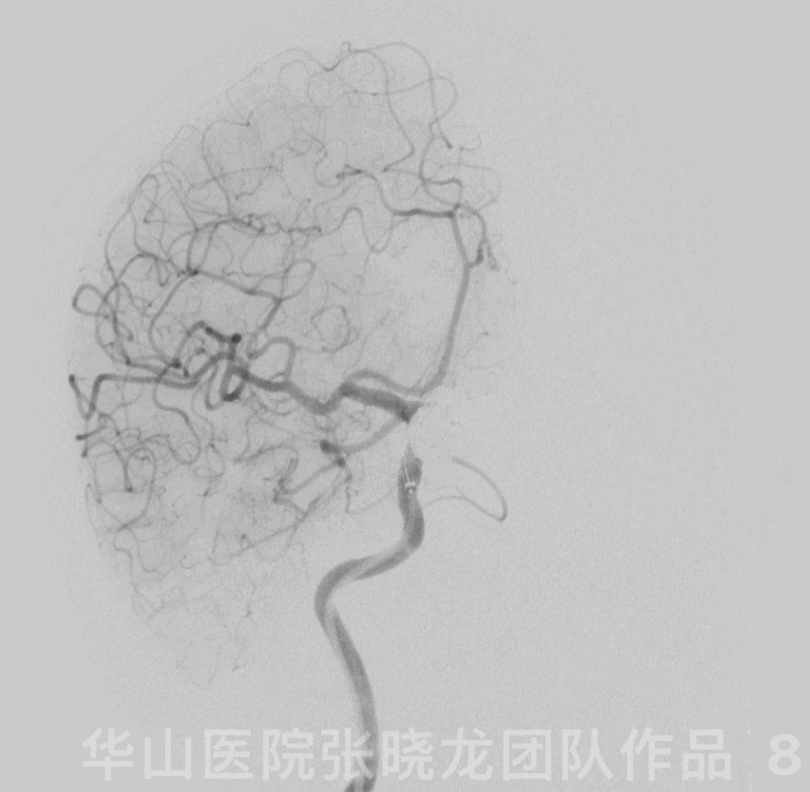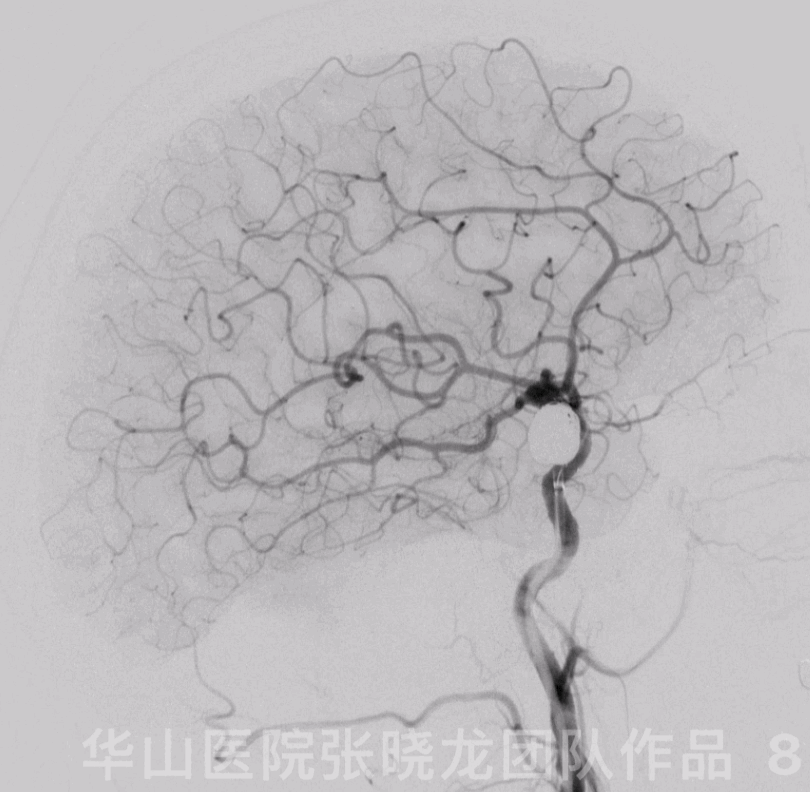
Figure 8 GIF. The aneurysm was packed densely and the parent artery patent.

Figure 9 GIF. Intracranial vessels were intact.
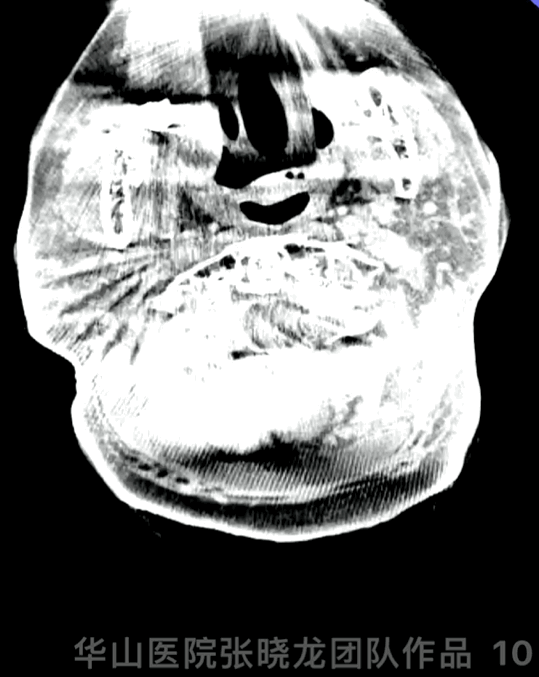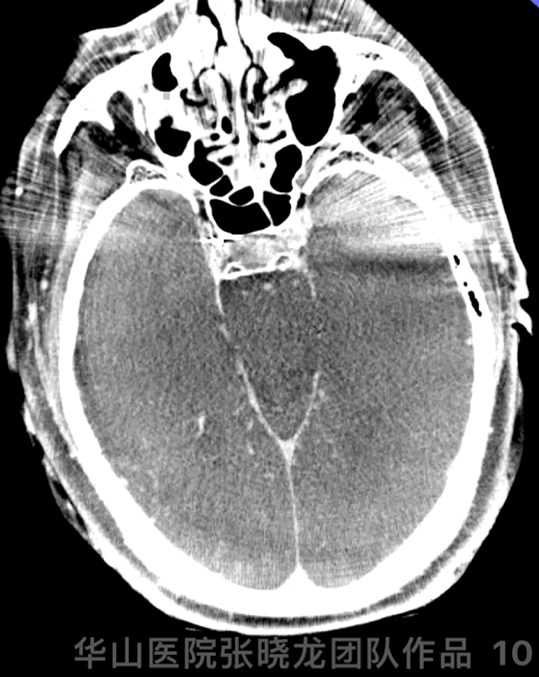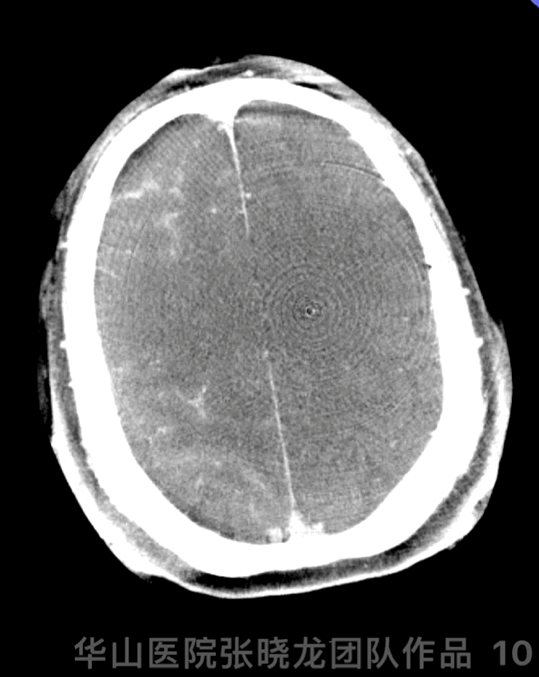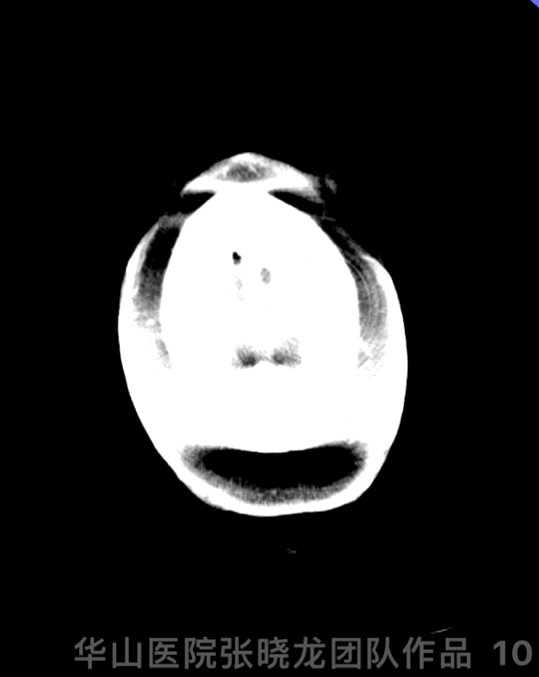
Figure 10 GIF. DynaCT demonstrated no hemorrhage.
3
Post Operation
GCS 15, no blurred vision, no new neurological defect. Tirofiban maintained 48 hours.
TEG: ADP 37%, AA 100%
At discharge: Aspirin for long time and Clopidogrel for 3 months.
4
Follow-up (9-month)
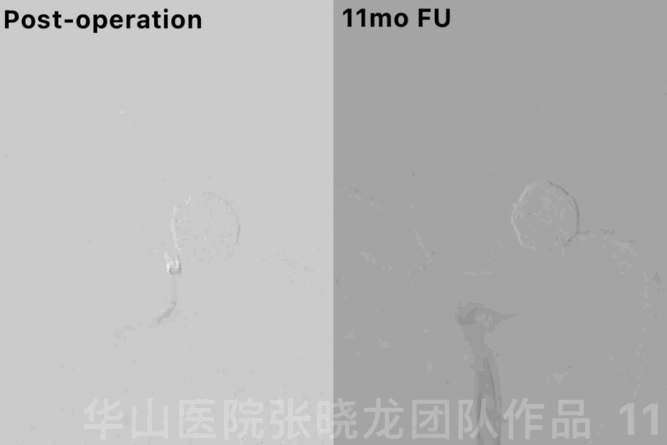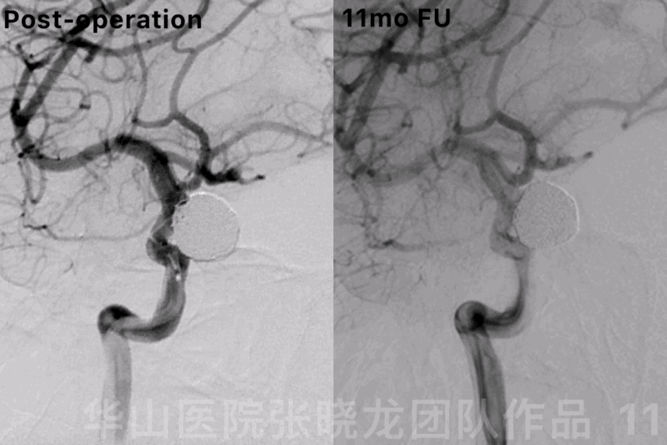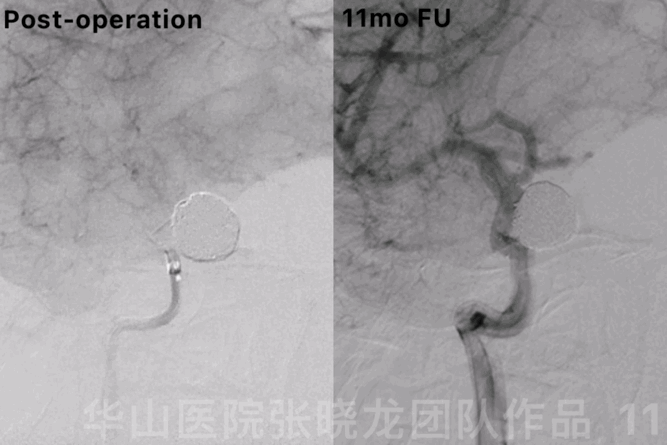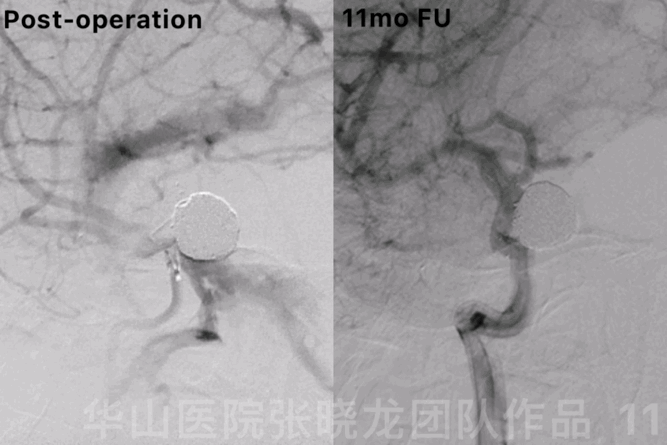
Figure 11 GIF. 11-month follow up angiography showed no relapse of the aneurysm.
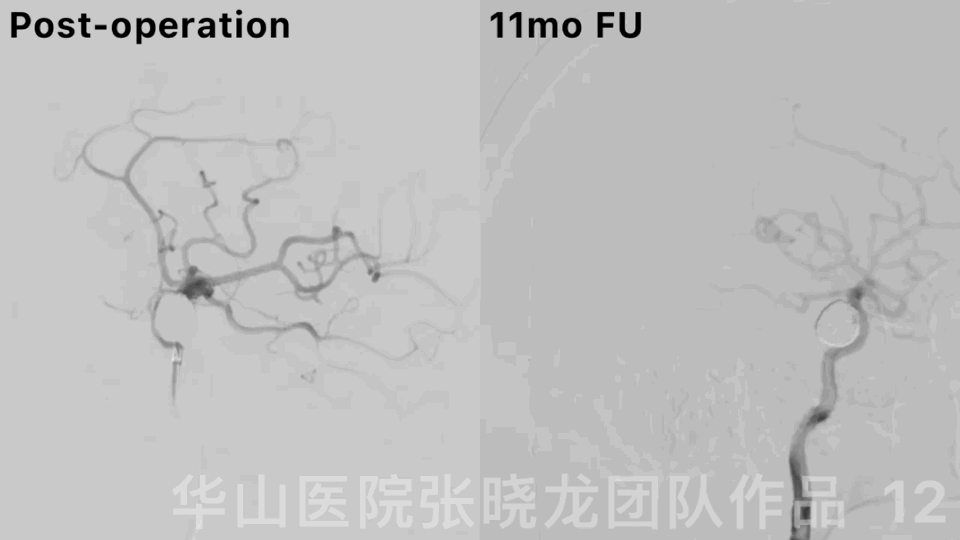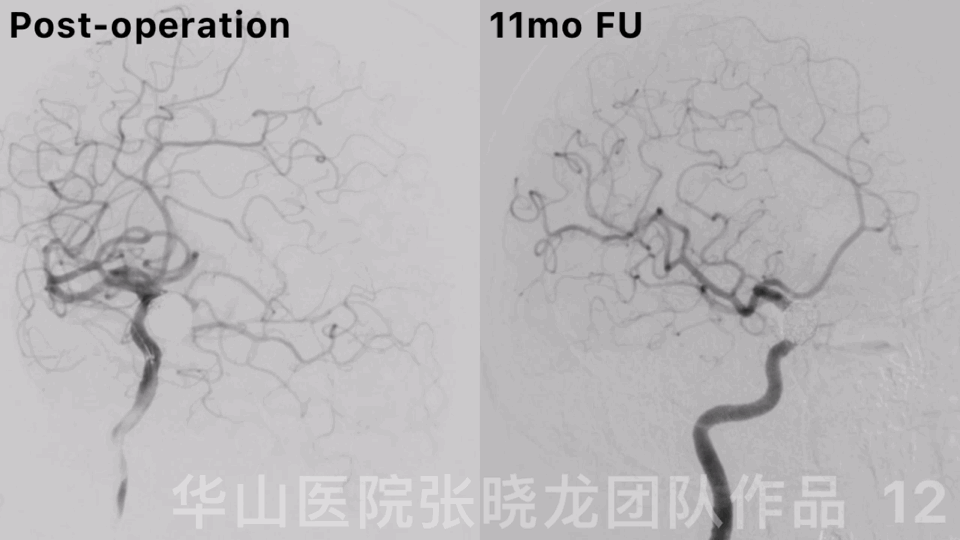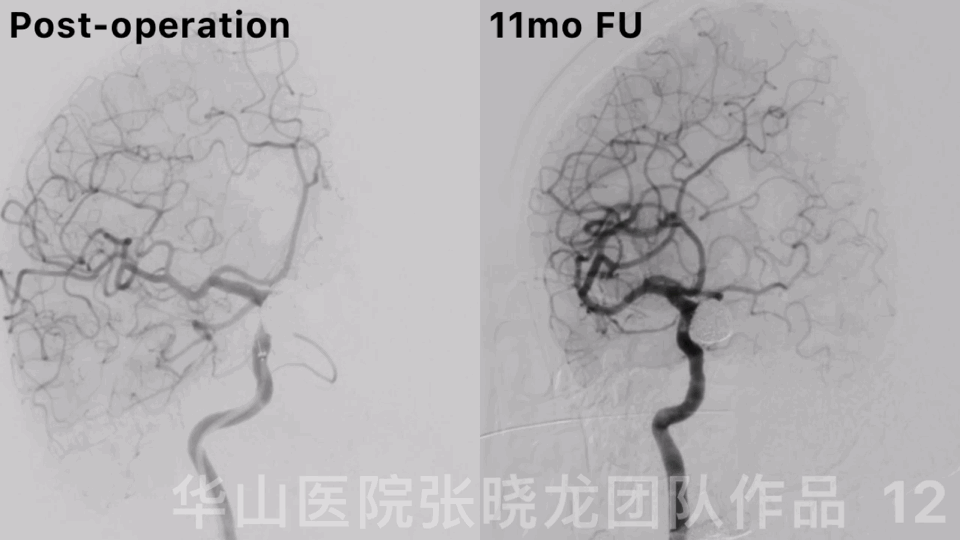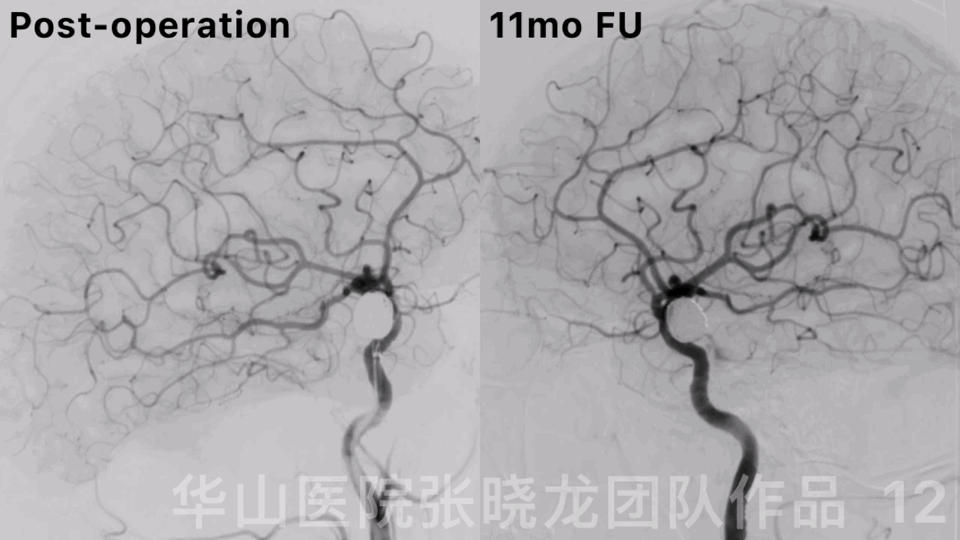
Figure 12. Rotational DSA displayed a densely packed large right ophthalmic aneurysm with the parent artery patency.
Summary
Large carotid ophthalmic aneurysm should be treated to avoid rupture and further mass effect.
Dual microcatheter technique was adopted to coil this large aneurysm.
Guiding catheter should be advanced as far as possible to supply strong support.
Stent assisted large coiling technique via large stiff coil microcatheter (prowler plus) could lower recurrence risk and was economical.
Pipeline was another choice for this kind of large ophthalmic aneurysms.
Long-term DSA angiography follow-up manifested the large ophthalmic aneurysm densely packed with parent artery patency. Discontinued Aspirin.
Next follow up was scheduled in 3 years.
